Name | Description |
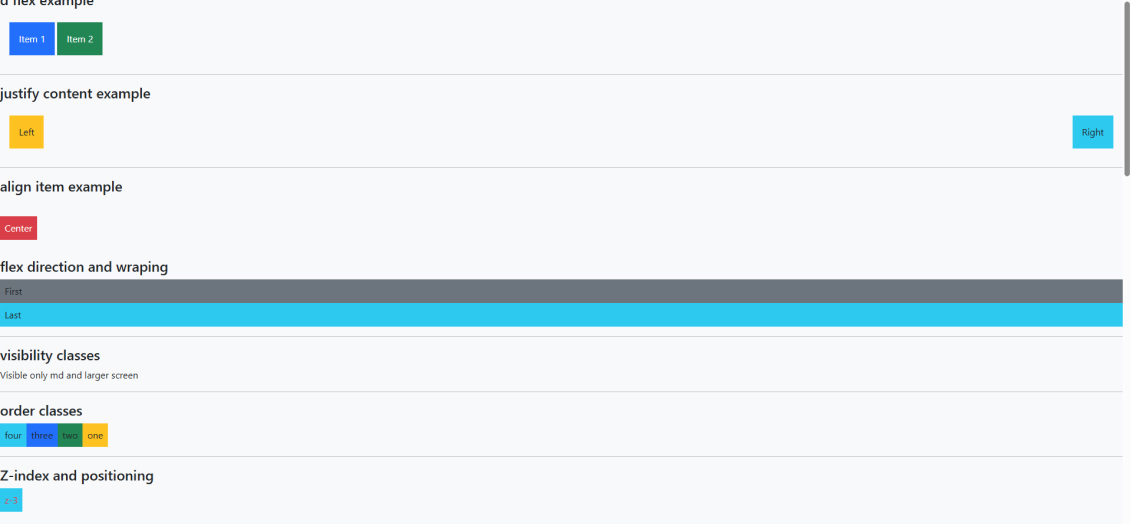
justify-content-start | Aligns flex items to the start (left) |
justify-content-center | Centers flex items horizontally |
justify-content-end | Aligns flex items to the end (right) |
justify-content-between | Distributes items with space between them |
justify-content-around | Distributes items with space around them |
justify-content-evenly | Distributes items with equal space around |
align-items-start | Aligns items to the top |
align-items-center | Centers items vertically |
align-items-end | Aligns items to the bottom |
align-items-stretch | Stretches items to fill container height |
flex-wrap | Allows items to wrap to multiple lines |
flex-nowrap | Keeps all items on single line |
order-0 to order-5 | Controls visual order of flex items (lower = first) |
order-{breakpoint}-* | Responsive ordering (e.g., order-md-1) |
d-none | Hide element on all screen sizes |
d-{breakpoint}-block | Show as block on specified breakpoint and up |
d-{breakpoint}-none | Hide on specified breakpoint and up |
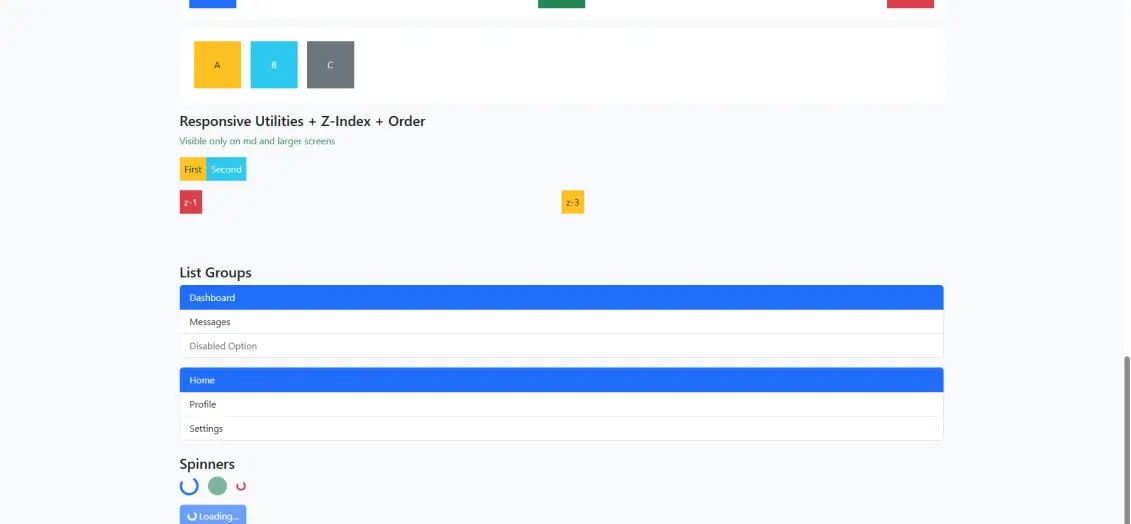
z-0, z-1, z-2, z-3 | Z-index values for stacking order |
top-0, top-50, top-100 | Vertical positioning values |
start-0, start-50, start-100 | Horizontal positioning values (left in LTR) |
table-primary, table-success, etc. | Colored table backgrounds |
table-sm | Compact table with reduced padding |
list-group-item-primary | Primary colored list item |
list-group-item-success | Success (green) colored list item |
list-group-item-warning | Warning (yellow) colored list item |
list-group-item-danger | Danger (red) colored list item |
active | Marks current/selected state |
disabled | Disables and grays out element |
text-primary, text-success, etc. | Text/spinner color variants |
role=”status” | ARIA role for loading indicators |
gap-* | Spacing between flex items (e.g., gap-3) |
m-* | Margin utilities (1-5) |
p-* | Padding utilities (1-5) |
mb-*, mt-*, ms-*, me-* | Directional margin utilities |
bg-light, bg-white, bg-primary, etc. | Background color utilities |
text-white, text-dark | Text color utilities |
rounded | Adds border radius for rounded corners |
shadow-sm | Adds subtle box shadow |