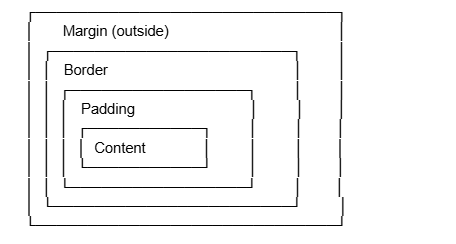
a {
color: #3498db;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
padding: 10px 15px;
border: 2px solid #3498db;
border-radius: 5px;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
display: inline-block;
}
a:hover {
background-color: #3498db;
color: white;
transform: scale(1.05);
}
/* Button Styles */
button {
background-color: #e74c3c;
color: white;
border: none;
padding: 12px 30px;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
border-radius: 25px;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #c0392b;
transform: translateY(-2px);
box-shadow: 0 6px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15);
}
button:active {
transform: translateY(0);
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
/* Input Field Styles */
input[type="text"] {
padding: 12px 15px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 2px solid #bdc3c7;
border-radius: 8px;
width: 300px;
transition: border-color 0.3s ease, box-shadow 0.3s ease;
}
input[type="text"]:focus {
outline: none;
border-color: #3498db;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgba(52, 152, 219, 0.2);
}
/* List Styles */
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
width: 300px;
}
li {
background-color: #ecf0f1;
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
border-left: 4px solid #3498db;
border-radius: 4px;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
li:hover {
background-color: #d5dbdb;
padding-left: 20px;
border-left-color: #2980b9;
}
/* Body General Styles */
body {
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
padding: 40px;
background-color: #f8f9fa; }