Business and technical perspectives are two perspectives that should be considered by the enterprise when deciding on microservices or composable architecture. It is not just a technological issue, but it also affects the speed of the development, the collaboration of teams, and the opportunity to adapt to the changing requirements of the market.
1. Evaluate Business Goals
Question: Are you concerned with fast delivery of new business functionality, or technical scalability and system resilience?
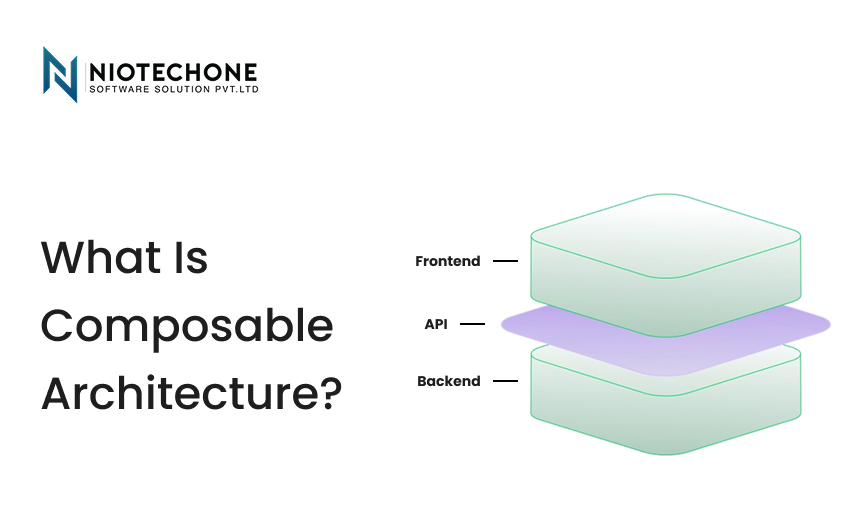
Composable architecture can help you to quickly develop new workflows and capabilities when you are interested in business agility.
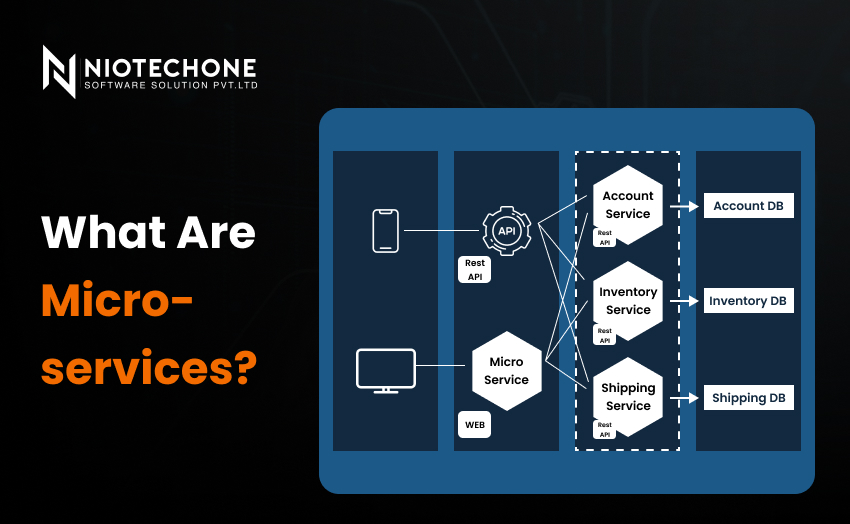
When you are interested in scaling complex technical systems, microservices offer independent services that can expand and develop without impacting other components of the application.
2. Consider Team Structure
Microservices: Teams may own particular services, which allow them to develop them in parallel, but they need to have experience with distributed systems and API communication.
Composable Architecture: Teams can work on reusable modules or components, working more closely with business stakeholders to create value more quickly.
3. Integration Strategy
Both architectures are based on APIs to communicate; however, their integration issues are different:
Microservices need orchestration and monitoring tools to coordinate service interactions.
Composable modules require good governance to provide uniformity in behavior across applications.
4. Scalability & Performance
Microservices are also good at scaling single services according to demand and are therefore suitable in high-traffic applications such as travel portals or e-commerce websites.
Composable architecture enables businesses to scale business processes effectively, particularly when implementing several front-end applications that share the same backend functionality.
5. Governance and Standardization.
Microservices: API contracts, service versioning, and deployment pipelines should be standardized to prevent chaos as the services increase.
Composable Architecture: This is to make sure that modules are reusable and consistent across applications to avoid duplication and integration problems.
6. Combination Strategy to the greatest good.
A lot of businesses are discovering that a combination of microservices and composable architecture provides the best of both worlds:
Scalability of technical backends, transaction processing, and core system functionality Use microservices.
Composable architecture is used to quickly build business-facing applications, user interfaces, or mobile solutions.
Example: A travel portal software may search flights, book hotels, and process payments with microservices, whereas composable modules process loyalty programs, personalized offers, and user dashboards. This combination provides speed and stability.
7. Measuring Success
The following metrics should be monitored by enterprises to assess the efficiency of the selected architecture:
- Frequency and speed of deployment.
- Reliability and uptime of the system.
- New feature time-to-market.
- Collaboration efficiency and team productivity.
- Customer satisfaction and user interaction.
With these metrics, organizations can constantly streamline their architecture, which guarantees long-term scalability and business agility.