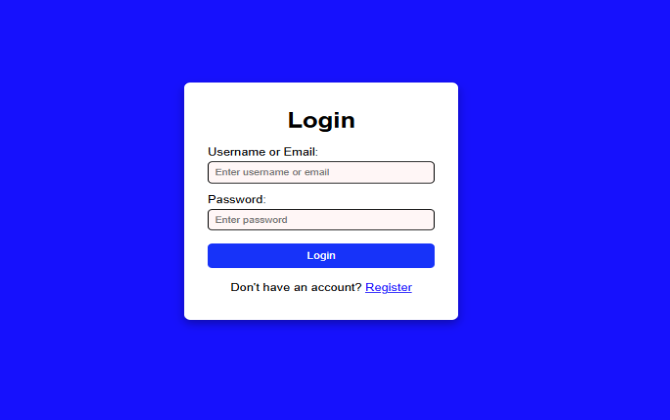
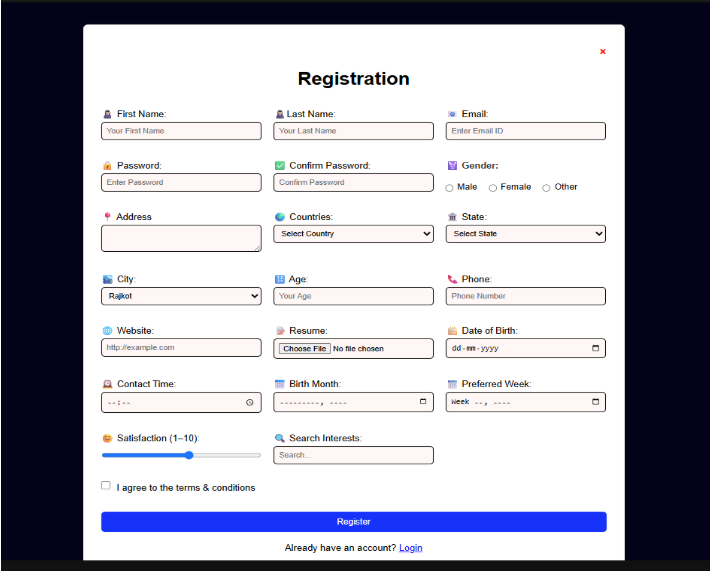
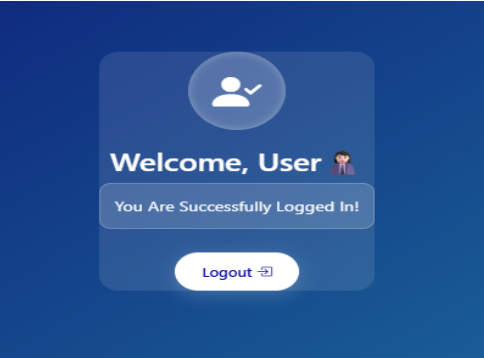
body {
font-family: 'Poppins', sans-serif;
background: linear-gradient(145deg, rgb(5, 5, 111), rgb(19, 130, 167));
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.card-container {
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
backdrop-filter: blur(16px);
border-radius: 20px;
padding: 40px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
.icon-circle {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border-radius: 50%;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
margin: 0 auto 20px;
font-size: 50px;
box-shadow: inset 0 0 10px rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
}