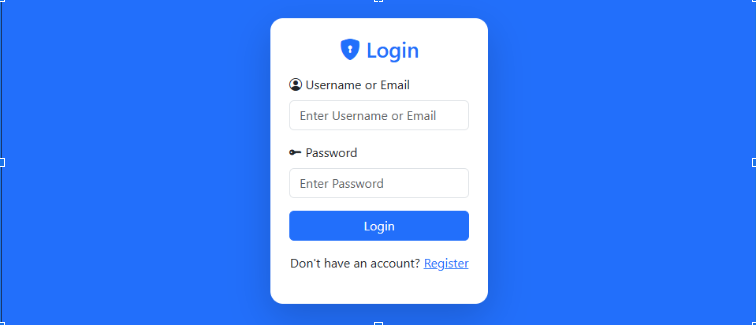
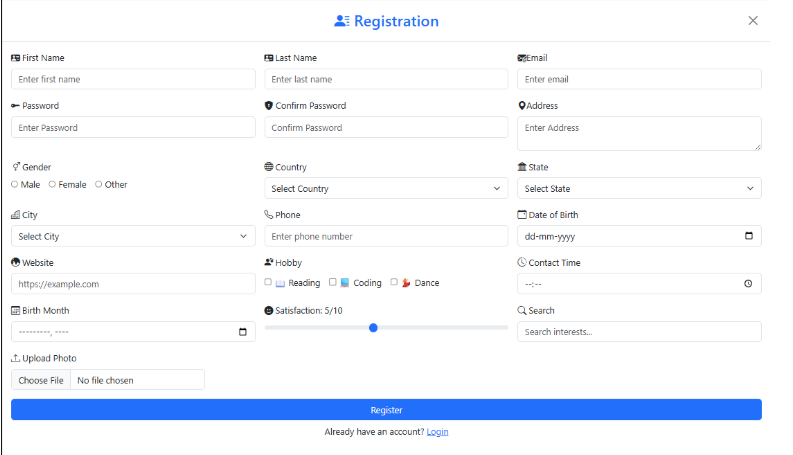
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="photo" class="form-label"><i class="bi bi-upload"></i> Upload Photo</label>
<div class="d-flex align-items-center gap-2">
<div class="flex-grow-1">
<input type="file" id="photo" class="form-control" accept=".png, .jpg, .jpeg" style="max-width: 350px;">
<div id="fileType" class="invalid-feedback">Please upload a valid photo (PNG, JPG, JPEG, max 100MB).</div>
</div>
<img id="preview" class="img-thumbnail d-none" style="width: 60px; height: 60px; object-fit: cover;">
</div>
</div>